Depression is a common mental health disorder. Approximately 17.3 million American adults are affected, and around 20% are being treated for the condition with medications from different antidepressant classes. It’s a common misconception that depression is simply a feeling of sadness. While sadness is typically a normal temporary reaction to loss, difficult situations, and disappointment, depression is long-lasting and requires treatment. Keep reading to learn more about depression and the most common antidepressants.
Depression and Its Symptoms
Depressive disorder, also known as depression, is characterized by persistent and severe feelings of sadness. It affects all aspects of your life, including how you think, feel, and react. Without treatment, depression can lead to thoughts of suicide, self-harm, risky behaviors, and even health problems.
There are several types of depression. Some develop as a response to specific circumstances. For example, postpartum depression develops within 4 weeks after a woman delivers a baby. Seasonal affective disorder occurs in the fall when temperatures get colder and lasts until spring or summer.
Clinical depression is the most common and most severe form of depression. Individuals with clinical depression experience symptoms for at least 2 consecutive weeks. These symptoms include a lack of interest in things that once brought joy, insomnia, and changes in appetite. Other types of depression include persistent depressive disorder (PDD), which lasts for 2 or more years, and disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD), which causes irritability and emotional outbursts.
Common Symptoms of Depression
Other common symptoms of depression include:
- Feelings of hopelessness
- Low self-esteem
- Feelings of guilt
- Difficulty making decisions
- Anxiousness
- Lack of motivation
- Moving or speaking more slowly
- Weight loss or gain
- Unexplained aches and pains
- Constant fatigue
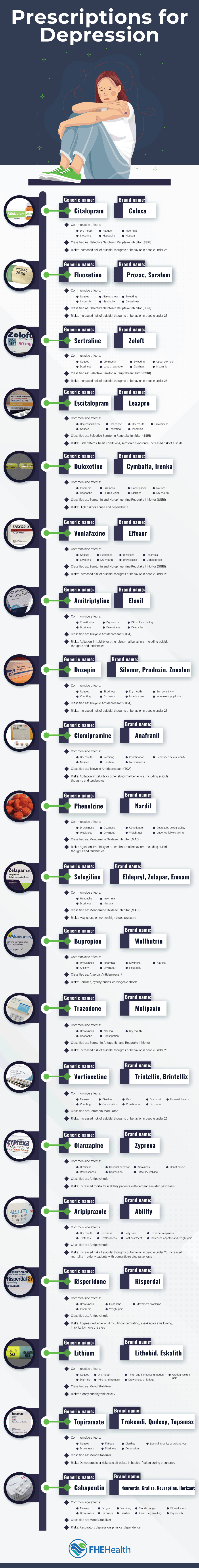
Antidepressant Classes
There are five main antidepressant classes, and each works in different ways and has its side effects. If you’re being treated for depression, you may have to try several different types of antidepression medications before you find the one that works for you.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are the most common antidepressants and are relatively safe. Commonly used SSRIs include citalopram, fluoxetine, sertraline, and escitalopram. These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that causes feelings of happiness. While all medications carry some risk of side effects, the side effects of SSRIs tend to be less severe than other antidepressants. These include insomnia, headaches, dry mouth, dizziness, joint pain, and upset stomach.
Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Antidepressant SNRIs have a calming effect, which helps relieve feelings of irritation and extreme sadness. Aside from depression, SNRIs are also frequently used to treat chronic nerve pain, such as fibromyalgia. They work by increasing serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain. Common names include duloxetine and venlafaxine. The side effects of SNRIs may be slightly more severe than those of SSRIs. While these depression medications are relatively safe for most people, they may cause elevated blood pressure, liver problems, insomnia, excessive sweating, and changes in sexual function.
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)
Introduced in the 1950s, TCAs treat depression and pain and are more likely to cause side effects like constipation, sleepiness, and dry mouth. These antidepressants increase serotonin and norepinephrine by blocking acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that affects the communication between nerves and muscles. TCA anxiety medication names include amitriptyline, doxepin, and clomipramine.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)
MAOIs are in a different class than other antidepressants. These medications are used to treat panic disorders, phobias, and other medical conditions like Parkinson’s disease. They aren’t prescribed as often due to their severe side effects, which include involuntary muscle spasms, tingling sensation of the skin, low blood pressure, and rash. When combined with alcohol use, MAOIs may cause a sudden spike in blood pressure. Common names include phenelzine and selegiline.
Atypical Antidepressants
Atypical antidepressants are usually used as a last resort when other anxiety medications have failed. They work in different ways to restore the chemical balance in the brain. Some increase levels of dopamine, while others work by boosting serotonin. This class of drugs includes bupropion, trazodone, and vortioxetine. Possible side effects of atypical antidepressants include headaches and fatigue, dry mouth, fainting, changes in vision, and increased bruising.
Other Medications to Treat Depression
Some additional medications may be used to treat depression, either alone or in addition to antidepressants.
- Antipsychotics: These drugs are used to treat anxiety, psychotic episodes, and depression. Sometimes they work well for patients who fail to respond to normal treatment methods. Most individuals have fewer side effects on antipsychotic medication, but they tend to be more severe, including involuntary muscle movements, tremors, and muscle contractions. Antipsychotics include olanzapine, aripiprazole, and risperidone.
- Mood stabilizers: Mood stabilizers are ideal for those who have mood swings, such as going back and forth between mania and depression. They’re most often used to treat bipolar disorder, personality disorders, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Sometimes they’re used to control seizures or control impulses. Popular medications include lithium, topiramate, and gabapentin.
Possible Side Effects and Considerations When Taking Antidepressants
Before you begin taking antidepressants, your doctor will review your medical history and consider any medical conditions you may have, whether you’re pregnant or breastfeeding, your age, the type of work you do, and whether you drink alcohol. It’s not advised that you drink alcohol at all while taking antidepressants, but some medications are safer than others. SSRIs are generally safe if you plan on drinking moderately and only occasionally, for example. Almost all antidepressants cause side effects, but they vary from one drug to the next.
Antidepressants can also interact with other medications, including ibuprofen, so it’s important to discuss any over-the-counter drugs you take with your physician.
If you or someone you love has depression or is going through a depressive episode, you don’t have to go it alone. FHE Health provides mental health treatments to help you address your anxiety and depression. For more information on what we offer, contact us to speak to a counselor and get started today.






