Feeling depressed? Before you shrug it off or explain it away, make sure you’re not ignoring what may be your body and mind telling you to seek support. Thanks to advances in both therapies and medications, depression and its associated symptoms are treatable.
Who’s affected by this disorder? The answer may surprise you. According to a 2025 fact sheet from the World Health Organization, over 330 million people worldwide suffer from depression, with women 50% more likely to report experiencing it versus men. In the United States, these numbers get even more troubling. A 2024 report by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA) found 1 in 5 American adults experienced depression that year, with about a quarter of these cases considered serious in severity.
What Is Depression?
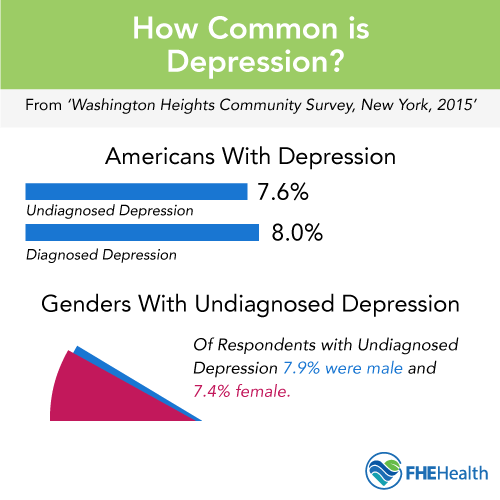
According to the Mayo Clinic, depression is defined as “a mood disorder that causes a persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest.” Like most mental health concerns, depression can vary widely in severity, from a mild, temporary condition manageable using methods such as talk therapy to a serious disorder with long-term, more intense symptoms requiring medical support.
Depression is one of the leading causes of disability, as well as a financial burden both on individual sufferers and the health systems supporting them. Unlike situationally appropriate sadness that passes quickly, depression can make everyday, short-lived emotional stresses seem to last longer, and it can occur even without an immediately apparent cause.
This persistence and longevity can make depression life-threatening. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), in 2023 alone, more than 49,000 lives in the United States were lost to suicide, often driven by mental health concerns such as depression. Thankfully, depression of all severities can be managed and treated using a wide range of therapies. If you’re living with depression, you don’t have to suffer in silence; help is available.
Types of Depression Explained
Depression is by no means a one-size-fits-all diagnosis. Different types can be brought on by different factors or manifest in differing levels of severity. Depression can also require various forms of treatments, which in turn can lead to different expected outcomes.
What Causes Depression?
Many factors can cause depression. A report from the National Institutes of Health indicates a number of elements contribute to the mental health disorder. Specifically, those with depression often have a combination of biological, genetic, psychological and environmental factors playing a role in the development of the condition.
Genetics and Predisposition
Those with a family history of any form of depression may be more likely to have the condition. This is why therapy often begins with discussing known health diagnoses from your closest blood-related family members.
Life Events
Major changes in a person’s life can trigger a depressive state. These may include both good and bad events, such as the birth of a baby, a divorce or the death of a loved one.
High-stress events, such as dealing with illness, moving or even changing jobs, can be a trigger. Additionally, in some people, physical or mental trauma can lead to depression months or even years after an incident.
Chemical Imbalances
A hormone imbalance can cause depression symptoms. This may occur as a result of changes in health, such as giving birth or having a malfunctioning thyroid. In other cases, prescribed medications can change a person’s chemical balance, leading to symptoms of depression.
Am I Depressed — A Depression Test
Many people try to find a simple depression test to determine if they have symptoms. But depression is complex and seldom something you can safely self-diagnose. Not only are medical professionals trained to provide assistance, they can help you impartially consider your personal circumstances, as well as look for other contributing health concerns. Your therapist can examine what’s occurring and determine the correct depression diagnosis, ultimately leading to the most beneficial treatment.

Effects of Depression
If you recognize the signs of depression in either yourself or a loved one, it’s important to take action. Depression doesn’t just go away — it builds. Over time, it can present a risk to your quality of life.
If left untreated, depression can lead to both mild and severe outcomes. These include:
- Excessive weight gain or loss
- Social isolation
- Social anxiety and phobias
- Substance abuse
- Difficulty with relationships
- Difficulty with work or school life
- Conflicts in day-to-day life
- Self-destructive behaviors such as reckless actions or cutting
- Suicidal feelings
- Poor health outcomes and premature death
Recognize the Signs and Symptoms of Depression
Depression develops from a wide range of aspects, leading to numerous symptoms. The most common include:
- Sadness, hopelessness
- Anger, often leading to outbursts and aggression
- Lack of energy
- Sleep problems, in some cases, too little or too much
- Loss of interest in things once enjoyed including hobbies, sex, sports or relationships
- Difficulty focusing; inability to make decisions
- Feeling worthless or having significant guilt
- Anxiety and restlessness
Treatment Options for Depression
 The first step is a proper diagnosis from a licensed psychologist or other therapists. This includes a physical exam, lab tests to spot hormonal imbalances and a full psychiatric evaluation. Once the therapist diagnoses the type of depression, a comprehensive treatment plan can be developed.
The first step is a proper diagnosis from a licensed psychologist or other therapists. This includes a physical exam, lab tests to spot hormonal imbalances and a full psychiatric evaluation. Once the therapist diagnoses the type of depression, a comprehensive treatment plan can be developed.
Treatment for depression may include medications and counseling. Patients who are facing severe symptoms or are at risk of harming themselves may need to remain in a hospital setting until doctors can stabilize them. Most people benefit from ongoing outpatient therapy.
Medications such as antidepressants are helpful to many individuals. These include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Doctors may need to spend some time adjusting medications to find the right one for your needs.
Psychotherapy is nearly always a part of treatment. It involves exploring the crisis, using cognitive behavioral therapy to develop new ways of thinking and setting realistic goals. In addition, alternative treatments, such as deep brain stimulation therapy, high-frequency pulsed-electromagnetic stimulation therapy and neurofeedback, may help some people.
Your doctor works to help determine the best possible treatment for your needs. Many times, treatment plans include various forms of care to create a method that helps you.
Seeking Help from FHE Health for Depression
If you’re concerned you may be depressed, chances are good you can benefit from one-on-one help and support. FHE Health can provide you with a strong path forward through our comprehensive treatment options. If depression is impacting your life, contact us today and let our compassionate team of counselors help you.








