Motivational interviewing (MI) is a client-centered, directive therapeutic approach that aims to help individuals resolve their feelings of ambivalence about change. Unlike some other therapeutic approaches that may rely more on confrontation or interpretation, MI emphasizes empathy, collaboration and evocation to overcome stumbling blocks in normal therapy approaches and keep progress moving forward.
Motivational Interviewing is a relatively new therapeutic approach many professionals have developed to help reluctant or resistive subjects overcome negative behaviors. This approach aims to help people resolve feelings of ambivalence about change by guiding them into a better understanding of emotional or personality traits that cause issues in their recovery or relationships. It’s most often used in counseling and health care settings to explore and strengthen a person’s motivation for change.
Understanding Motivational Interviewing
Motivational interviewing is a novel approach to overcoming negative reactions to therapy by guiding subjects to a better understanding of the reasons they have for resisting progress in their care. It’s based on an acceptance that ambivalence is a common stumbling block for many people in therapy and that valid strategies need to be developed to overcome it. This helps people clear blocks and get back on track toward further progress.
The motivational interviewing approach relies on a strong-willed therapist who can build empathy, collaboration and positive evocation while avoiding direct confrontation or coercive techniques. The idea behind it is that people move through stages of change and the appropriate therapeutic approach will change as the person getting therapy makes progress.
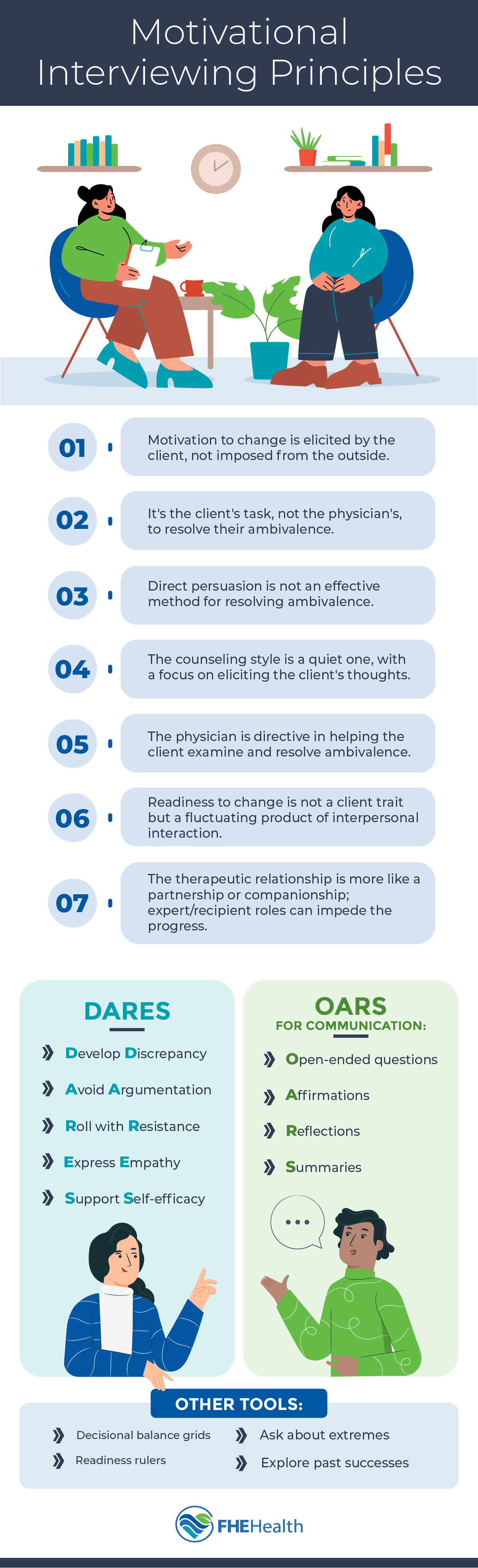
Principles and Techniques
The key principles of MI include expressing sincere empathy, developing a patient’s sense of discrepancy between their current behavior and their stated goals, rolling with resistance and supporting self-efficacy. These principles guide the practitioner in helping the client explore and resolve their resistance to making a positive change.
Therapists working with MI aim to express empathy and develop their patients’ understanding of the disconnect between their current state and their stated therapy goals. The technique’s purpose is to encourage self-awareness and a better perspective on the progress they’ve been making. In practice, the approach uses reflective listening, affirmations and a concise summary of a subject’s own thoughts. Motivational interviewing questions tend to be open-ended, encouraging independent thinking and searching self-reflection. The point is generally to develop clarity about the patient’s therapeutic goals and keep making progress toward them.
In practice, MI involves using techniques such as reflective listening, asking open-ended questions, affirmations and summarizing to help clients explore their motivations for change. The practitioner works collaboratively with the client to strengthen their motivation and commitment to the therapeutic process they’ve committed to. To help remember the techniques most at play in MI, remember the acronym OARS, which stands for:
- Open questioning
- Affirmations
- Reflections
- Summarizing
Application in Various Settings
People have benefited from motivational interviewing in a range of settings. Aside from the obvious application MI has for mental health services, it can also be found in health care settings. Here, practitioners can use it to help bring patients along during prolonged or chronic illness and help improve compliance with a treatment plan. It also turns up in addiction and substance abuse treatment, criminal justice settings and behavior modification treatments, such as for smoking cessation and obesity and during the adjustment period while people get used to a new treatment routine. It’s also about 10%-20% more effective at reducing risky lifestyle behaviors among people in therapy for addiction and similar treatment programs than conventional methods.
In couples therapy, OARS motivational interviewing can be helpful in addressing subjects’ ambivalence and resistance to a searching inventory of the progress a couple is making. It can also work as an adjunct approach to other therapies, such as during life changes, major career changes and relationship issues.
Benefits and Effectiveness
Some research shows MI can be highly effective in treating addiction and other behavioral issues. It’s been found to increase motivation for change, improve treatment adherence and lead to better outcomes in various behavioral interventions. Multiple studies have been done to gauge the effectiveness of MI in treatment for people in a diverse range of situations.
Studying MI is made somewhat more difficult by the flexibility of the OARS approach because it can be applied partially or in whole, as well as in conjunction with other therapeutic approaches. Some studies show that motivational interviewing is effective in some settings, such as among older teens and young adults, but the numbers tend to drop in other contexts.
Considerations and Limitations
As helpful as it can be in multiple settings, motivational interviewing isn’t the only option for people seeking positive therapy outcomes. It’s also not a one-size-fits-all approach that unfailingly works for everybody. Instead, the MI approach should be taken only by a skilled practitioner who knows the technique well and can apply it where appropriate. It’s also not generally effective for people who are highly resistant to change or who have complex mental or emotional health issues that call for a different approach to care.
Training and Certification
MI is a therapeutic approach rather than a specific discipline in itself. Even though it’s contained within the larger field of mental health therapy, practitioners can still train in it as a standalone approach and even get certification in the technique. This training typically includes theoretical background, practical skills development and supervised practice in a clinical setting.
Using Motivational Interviewing to Improve Outcomes
If you or a loved one is working through mental or emotional health issues or dealing with a substance abuse issue that’s resistant to therapy, you might need more help than you’ve had so far. Contact the friendly and compassionate staff at FHE Health for advice, referrals and more information about motivational interviewing, as well as the multitude of other therapeutic approaches we can help you with.