Everyone experiences a small amount of anxiety at various points throughout their lives. For many people, these feelings pass and they can easily move on. However, for the 32 percent of individuals who have anxiety disorders, the weight of anxiety never fully goes away. Often, the symptoms actually get worse over time. Depending on the severity, anxiety disorders can affect your schoolwork, job performance, and relationships.
Thankfully, anxiety is treatable. Most people find relief in treatment options like cognitive behavioral therapy or similar talk therapies. Others benefit from support groups and stress-managing hobbies. If the symptoms are proving particularly bothersome, psychiatrists will often prescribe medications.
Doctors use a variety of anxiety medications, depending on the patient’s needs, goals, and medical history. Some of these medications are more powerful at reducing symptoms but have more severe side effects, while others are safer but may not be as effective. Understanding these medications along with their effects, downsides, and other characteristics will allow you and your doctor to make the best decision for your health.
Common Anxiety Medications
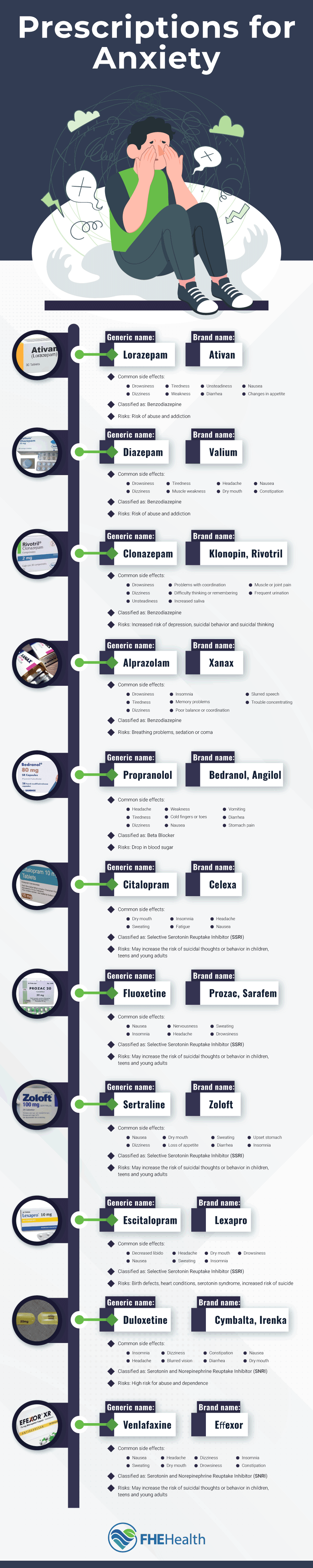
Generally speaking, there are four common types of anxiety medications: selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, benzodiazepines, and beta blockers.
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
SSRIs are antidepressants that also carry anti-anxiety benefits. By increasing levels of serotonin in the brain, these drugs can boost your mood and limit symptoms of anxiety.
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Another type of antidepressant, SNRIs are similar to SSRIs. Rather than just increasing serotonin, SNRIs also raise norepinephrine levels in the brain. Norepinephrine is a core part of the fight, flight, or freeze response, and adjusting it along with serotonin can cause a notable anxiety reduction.
Benzodiazepines
These drugs work as central nervous system depressants, meaning they basically slow down the brain activity responsible for your anxiety.
Beta blockers
Unlike the others on this anxiety medication list, beta blockers were not originally antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs. Instead, they reduce blood pressure. This can be good for managing the more physical symptoms of anxiety, like a rapid heartbeat or trembling.
How the Medications Work
SSRIs and SNRIs
Both SSRIs and SNRIs boost serotonin levels. Serotonin is a chemical messenger or “neurotransmitter” that relays messages between neurons. Normally, these neurons will reabsorb serotonin. SSRIs and SNRIs prevent this from happening, freeing up more serotonin for better messaging between neurons. SNRIs also do this for norepinephrine, another neurotransmitter.
Benzodiazepines
As central nervous system depressants, benzodiazepines limit the activity of your central nervous system. They accomplish this by telling the brain to release a neurotransmitter, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which has sedative, hypnotic, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant, and muscle relaxant abilities. Basically, benzodiazepines can treat a wide range of symptoms, especially in cases of depression and anxiety.
Beta Blockers
Each beta blocker works slightly differently, but they all focus on reducing blood pressure. Most accomplish this by blocking the hormone epinephrine, known more commonly as adrenaline. This slows down your heart beat. Some beta blockers also widen your blood vessels to improve blood flow.
Benefits and Side Effects of Each Medication
As with all medications, each anti-anxiety drug comes with both therapeutic benefits and side effects.
SSRIs
SSRIs are some of the most common anti-anxiety medications because they are safe and quite effective in managing conditions like generalized anxiety disorder. Importantly, most SSRIs are not chemically addictive, unlike many other drugs. In terms of side effects, you may experience sexual dysfunction, headaches, sleep issues, dizziness, gastrointestinal problems, and dry mouth. In rare cases, people have reported experiencing worsened anxiety.
SNRIs
Like SSRIs, SNRIs are extremely safe and effective medications. While some opioid SNRIs are addictive, most are not. Both classes of drug share many potential side effects, such as sexual dysfunction, dizziness, and headache. Depending on your unique circumstances, the increase of norepinephrine levels can sometimes cause added anxiety and higher blood pressure.
Both SNRIs and SSRIs can result in a rare, but serious, complication called serotonin syndrome, which occurs when there is excess serotonin in the body. Symptoms of this range from nausea and vomiting to fever, seizures, and delirium.
Benzodiazepines
Because benzodiazepines are so powerful, they have much more notable benefits while also carrying more serious risks. Improvements in anxiety symptoms often occur very quickly. They also treat problems that other drugs might not, such as insomnia.
Most of the side effects stem from their muscle relaxation and sedative abilities. Drowsiness and dizziness are typical, as is a drop in focus and alertness. Poor libido, erectile problems, or another form of sexual dysfunction is also possible. Over time, benzodiazepines may actually trigger feelings of depression and general anxiety, as well as agoraphobia, social anxiety, and thoughts of suicide.
Benzodiazepines are also very addictive and most people develop a tolerance to the drugs within a matter of weeks. For these reasons, doctors typically only prescribe these medications for short-term use.
Beta Blockers
Like many other cardiovascular drugs, beta blockers can affect blood flow to the extremities. You might notice this as cold hands or feet or even a slight bluish coloration in these areas. Some people have feelings of fatigue. Weight gain is also possible. Though rare, some people have reported worse feelings of depression, shortness of breath, and sleeping troubles.
Factors to Consider When Deciding on a Medication for Anxiety
When discussing your anti-anxiety medication options with your healthcare team, you have several factors to consider. The most important are probably your individual symptoms and their severity. If your anxiety is not affecting your day-to-day life, there may be no need to use medications at all. However, if your symptoms are actively hindering you from living your life, the pharmaceutical treatment path may be an effective way to manage them.
Additionally, doctors need to consider your medical history and current medications. For example, beta blockers may inhibit signs of low blood sugar in people with diabetes, so they may not be the best choice in these cases. If you have a history of substance abuse, more addictive benzodiazepines may not be right for you.
Your current medications also play a role in what anxiety medications to take. Interactions between drugs may inhibit their effectiveness or actively harm you. SSRIs and SNRIs can interact with painkillers, other antidepressants, and appetite suppressants among many others. Benzodiazepines can interact with contraceptives, antibiotics, antifungal agents, and antidepressants, as well as alcohol and opioids.
Lifestyle factors are also important. The sexual dysfunction side effects that occur with most anti-anxiety medications may be unacceptable for you. Discuss this with your doctor and find out what options are available.
Consult with an Expert
As you’ve almost definitely noticed, the advice “talk with a professional” pops up a lot when talking about managing anxiety. While you may have some wariness about talking about your problems with a stranger, there is no better way to make sure you get the help you need.
Anti-anxiety medications can be a powerful tool to help you lighten the load of anxiety symptoms. However, they can also pose dangers to your health if you do not have a licensed, trained professional to supervise your care. If you’re experiencing symptoms of anxiety that are interfering with daily life, consult your doctor or a mental health provider. They should be able to conduct a screening and, based on your symptoms, make a referral. You can also reach out to our experts at FHE Health anytime, day or night, for a free consultation.