
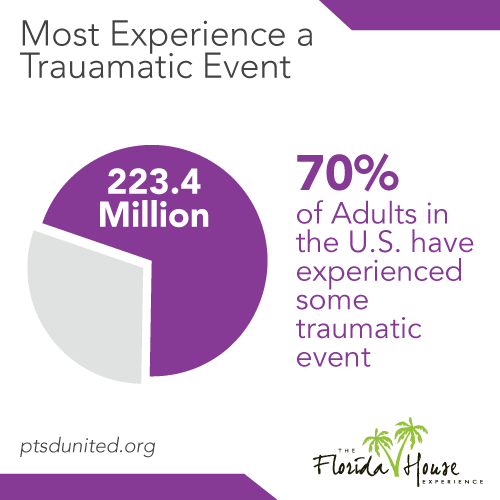
Are you among the 223.4 million Americans who have has experienced some sort of traumatic event at least once in their lives? Do you live with the after-effects of a traumatic event, experience, or years of abuse?
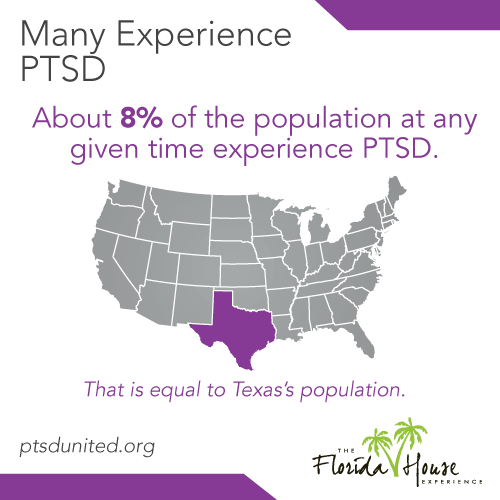
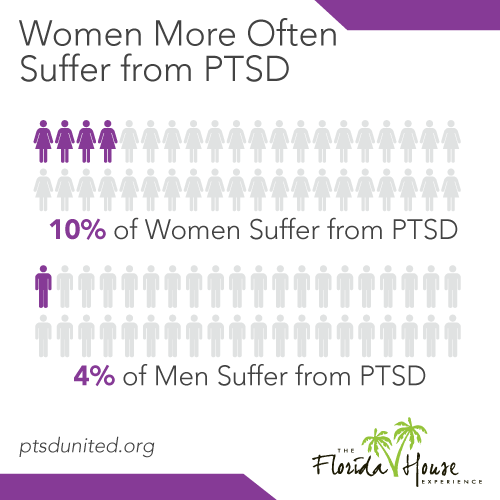
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) impacts an estimated five percent of all adults in the United States at any given time – that’s higher than the current number of people living with cancer. While those numbers may seem grim, the good news is that there are now a number of highly effective therapies for treating trauma available.
What Is Trauma?
According to the Australian Psychological Society, trauma is the exposure to specific events or situations that are extremely frightening, distressing, or upsetting, Traumatic events often pose a serious threat to your physical or psychological well-being, and often involve elements that are beyond your control.
Common examples of things that can trigger issues with trauma include:
- Being a victim of a sexual assault, robbery, or other crime
- Witnessing a death
- Involvement in a car crash
- Active military service
- Medical trauma (including being diagnosed with a life-threatening illness or undergoing a painful medical procedure)
Contrary to what you might believe (or have been told), trauma isn’t something that you can simply ‘get over’. Trauma affects everyone differently, and there is no shame in seeking out treatment for trauma.
What Are The Effects Of Trauma?
While everyone reacts to trauma in their own unique way, there are some common physical, emotional, and psychological symptoms associated with PTSD and other types of trauma-related conditions.
Emotional Signs of Trauma:
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Episodes of lost time or dissociation
- Hopelessness or despair
- Low self-esteem
- Isolation from others
- Intense feeling of abandonment or loss
- Desire to inflict harm self-harm
- Loss of meaning to live or sense of purpose
- Distorted sense of self or body image
- Feeling alienated from others or emotional numbness
- Chronic fatigue, insomnia, lethargy, loss of interest in normal activities
- Chronic anger or resentment
- Poor impulse control
- Obsessive thoughts or worries of an unwanted nature
- Night terrors, flashbacks, nightmares
- Inability to organize, plan or make decisions
Physical Symptoms of Trauma:
- Increased use of alcohol and/or drugs to numb the pain from intense feelings and try to cope
- Deliberate avoidance of situations that trigger traumatic memories
- Angry outbursts, crying, blaming others for their situation
- Wanting to be alone, staying away from friends
- No longer participating in formerly enjoyed activities
- Paleness, lethargy, fatigue
- An inability to cope in certain situations
It’s important to understand that traumatic stress affects everyone differently. Two people could have entirely unique responses to exactly the same environment, situation, or event. A number of variables impact an individual’s response to traumatic experiences, and it’s impossible to predict who will suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder and other forms of traumatic stress.
What is known is that “traumatic stress seems to have a lifetime cumulative effect”, and that “Previously traumatized victims seem more likely to develop PTSD than first-time victims”, meaning that the more frequently an individual is exposed to traumatic situations, the more likely they are to suffer from long-lasting emotional, psychological, and physical effects related to trauma.
Researchers have also discovered a link between levels of the stress hormone cortisol among traumatized victims and the risk of developing trauma-related depression and anxiety (PsychiatricTimes – Traumatic Stress and Human Behavior, Andrei Novac, MD). People who had high levels of blood cortisol immediately after exposure to a traumatic event suffered higher rates of PTSD than those who had elevated blood cortisol levels in response to a similar event.
What Happens If Trauma Isn’t Treated?
Left untreated, it’s common for people who struggle with substance abuse and mental health issues such as depression and anxiety to have a history of childhood trauma such as the sudden, violent loss of a loved one, experiencing a natural disaster, and being victimized by physical, sexual, or psychological abuse.
Children who grow up in stressful environments also often experience persistent symptoms of trauma well into their adult years. Living with addicted parents, being a part of a military family where a parent was deployed for weeks or months on end, and being involved with the child welfare system are all situations that can trigger trauma stress.
Need Treatment for Trauma? We’re Here For You
At FHE Health, we understand that many people who struggle with substance abuse and mental health issues have experienced trauma in their lives, and often, this trauma fuels a destructive pattern of addiction, negative thoughts, and harmful behaviors.
Our team of addiction and mental health specialists address trauma in all of our inpatient and outpatient programs. We use cutting-edge methods to thoroughly assess the impact of trauma, and use science-based therapies for trauma treatment in both group and individual counseling sessions.
If you or someone you care about needs trauma treatment, call us here at (833) 596-3502. We’re available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week to help you take the first steps on your trauma recovery journey.






