
Updated 2/5/2025
Mirtazapine is an antidepressant that’s commonly sold under the brand name Remeron. If you’re struggling with depression that’s further complicated by anxiety or insomnia, your doctor may suggest trying mirtazapine to manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
However, when it’s prescribed for the first time, you may have questions such as:
- Is Remeron a benzo?
- Is mirtazapine a narcotic?
- Is mirtazapine addictive?
- Do mirtazapine and alcohol interact?
Learning about the various Remeron uses and the drug’s role in popular culture can help answer these questions.
What Is Mirtazapine?
Mirtazapine is an antidepressant drug taken in pill form. It’s a newer tetracyclic piperazine-azepine antidepressant that was originally approved in the Netherlands in 1994. It was intended for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Today, it’s also used to treat other conditions, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder and anxiety disorders. It’s an SNRI, or a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.
Notably, the drug was found in actor and comedian Robin Williams’ system following his tragic suicide in 2014. While it isn’t addictive, users sometimes become physically dependent on it. For those individuals, stopping the drug suddenly can result in unpleasant symptoms over the short term.
As it’s a fairly new antidepressant, MarketWatch predicts that the market for mirtazapine will grow at a steady rate between 2021 and 2027.
What Does Mirtazapine Do?
Mirtazapine belongs to a group of drugs called tetracyclic antidepressants. The medication works on your central nervous system to impact chemicals in the brain that may be out of balance, resulting in depression.
Mirtazapine works by increasing the chemicals serotonin and noradrenaline in the brain. An imbalance of these chemicals can result in various mood disorders, and the drug works to restore a healthy balance. It’s suitable for most adults with depression, but some individuals shouldn’t take it.
This medication can make it more challenging for individuals with diabetes to effectively manage their blood sugar. It can also cause low blood pressure, which may be problematic for individuals with heart conditions. If you have glaucoma, you should discuss the benefits of taking mirtazapine versus the potential risks with your doctor. It can increase eye pressure, potentially worsening the condition.
Taking mirtazapine may also be dangerous for individuals with epilepsy or those who’ve taken other antidepressants recently. Before starting mirtazapine, have an honest conversation with your doctor about other medications you’re taking. If you’re pregnant or trying to become pregnant, you should also consult your doctor before taking mirtazapine.
 While you can’t become addicted to mirtazapine, it’s possible to overdose on the drug.
While you can’t become addicted to mirtazapine, it’s possible to overdose on the drug.  To determine if you or someone you know is abusing Remeron and needs professional help, watch for these indicators of mirtazapine abuse:
To determine if you or someone you know is abusing Remeron and needs professional help, watch for these indicators of mirtazapine abuse: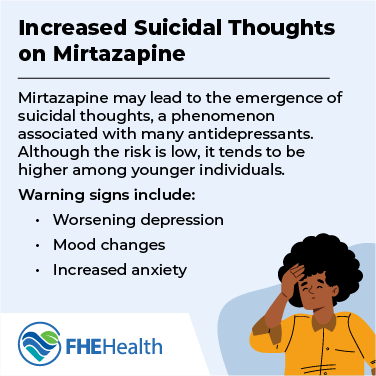 In rare cases, mirtazapine may lead to the emergence of suicidal thoughts, a phenomenon associated with many antidepressants. Although the risk is low, it tends to be higher among younger individuals.
In rare cases, mirtazapine may lead to the emergence of suicidal thoughts, a phenomenon associated with many antidepressants. Although the risk is low, it tends to be higher among younger individuals.





