Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), formerly known as attention deficit disorder (ADD), is a condition that reduces the brain chemicals responsible for regulating attention, organization, emotions and actions.
ADHD is one of the most common mental and developmental disorders. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) reports that 6 million people aged 3 to 17 have been diagnosed with ADHD over the years. According to the Anxiety & Depression Association of America (ADAA), 60% of children with ADHD grow up to become part of the 8 million adult Americans with ADHD.
ADHD affects your ability to pay attention, regulate your movements and control your impulses. However, it’s primarily a genetic condition, so it can’t be cured. Instead, experts use therapy and ADHD medication to manage its symptoms and help you lead a productive life.
Let’s explore some functions of common ADHD medications and what to expect when taking them to manage your symptoms.
ADHD Medications: Overview and Effectiveness
Stimulants are the most commonly prescribed medications for ADHD because they increase the brain chemicals affected by the condition, making it easier for you to think, plan, pay attention and control your movements.
ADHD drugs can function in two ways:
- Short-acting. The effect of these ADHD drugs can be felt less than an hour after they’re ingested and last for up to 6 hours. Because their effects wear off quickly, you may have to take them multiple times daily to manage your symptoms.
- Long-acting. The effects of long-acting ADHD medication are spread out, so some of them are felt immediately while the rest are slowly released throughout the day. Depending on your prescription, you can take one dose of a long-acting ADHD medication daily and receive its benefits for up to 16 hours.
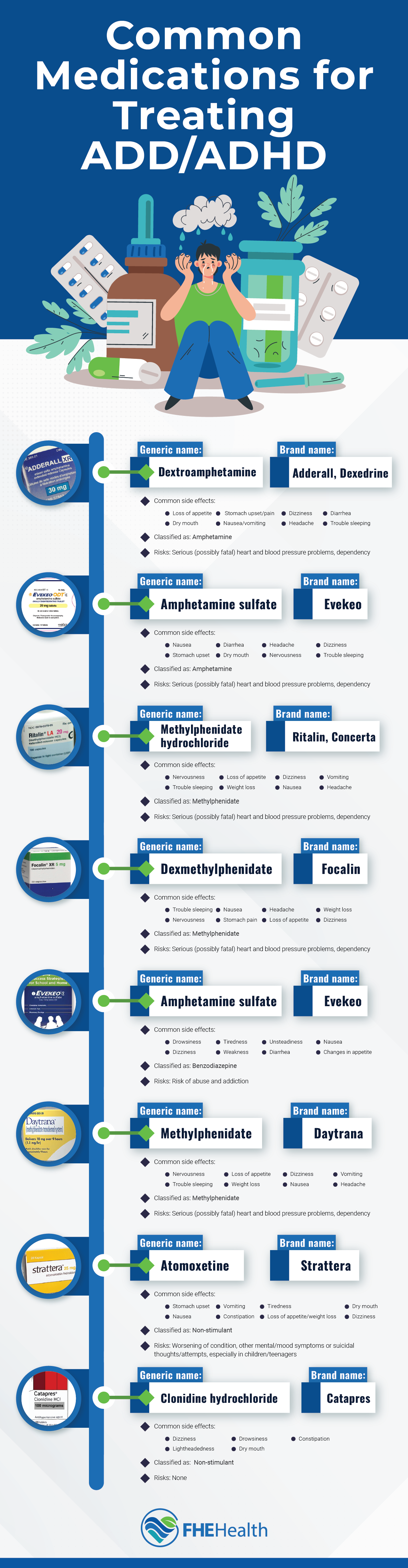
The most common stimulant ADHD medications belong in the amphetamine and methylphenidate categories.
Amphetamines
Amphetamines treat ADHD by increasing the brain chemicals dopamine and norepinephrine, causing you to become more alert, relaxed and confident. Taking amphetamines also improves your emotional and behavior regulation mechanisms, making you more capable of focusing on home, school or work tasks.
Amphetamine ADHD medication can be short- or long-acting. Adderall, Dexedrine and Evekeo are popular brands of short-acting amphetamines, while Adzenys XR-ODT, Adderall XR and Vyvanse are long-acting amphetamines.
There are some risks involved with taking amphetamines. Short-acting ADHD drugs can make you feel tired or depressed as they wear off. Long-acting ADHD medications can also affect your mood and disrupt your eating and sleeping patterns.
Methylphenidates
Methylphenidates block the reabsorption of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain. When these chemicals accumulate outside your brain cells, they improve your attention span, concentration and impulse control.
Ritalin and Focalin are brand-name methylphenidates that are effective for around 4 hours. Concerta, Daytrana and Ritalin LA are long-acting methylphenidates with effects that can last for more than 10 hours.
The side effects of methylphenidates include headaches, nausea, increased heart rate, mood changes, loss of appetite and weight loss.
Non-Stimulant Medications: Types and Benefits
Non-stimulant ADHD medications boost your energy levels and attention span by increasing the level of norepinephrine in the brain. While stimulants are fast-acting, it may take a few weeks of continued usage for you to start to feel the initial effects of non-stimulants. However, non-stimulants produce longer-lasting results than stimulants, with some taking up to a week to wear off.
Strattera is a common ADHD medication, and its effects can last for 24 hours. Clonidine is another popular non-stimulant ADHD drug. Some brands of clonidine can control your ADHD symptoms for up to a week.
Individualized Treatment Plans and Medication Selection
ADHD symptoms present differently, so treatment approaches differ from person to person. An individualized treatment plan allows your doctor or psychiatrist to monitor your responses to ADHD medication and adjust the dosage and prescription as the effects become apparent.
Most clinicians prescribe low doses of a long-acting methylphenidate to newly diagnosed ADHD patients. Your prescription may also include a short-acting methylphenidate that can control your symptoms before and after the long-acting dose takes effect.
If your symptoms respond well to methylphenidates, your physician will slowly increase the dose so you can fully benefit from the medication. However, if your symptoms don’t respond well even to higher doses of methylphenidate, your doctor will switch your prescription to a long-acting amphetamine.
Methylphenidates and amphetamines can be paired with non-stimulant medication to manage side effects. If you don’t respond well to any of the different types of stimulants, your doctor will only use a non-stimulant to manage your ADHD symptoms.
When it comes to treating ADHD in adults, medication may feel like a trial-and-error process. However, trying out the different drugs ensures you can find a prescription you’ll derive the maximum benefits from with minimal side effects.
Potential Side Effects and Monitoring for Optimal Results
All ADHD drugs have side effects that need to be carefully monitored. For example, stimulants and non-stimulants can decrease your appetite, cause weight loss and affect the quality of your sleep. The medication can also cause physical symptoms such as dry mouth, nausea, headaches, stomachaches and increased heart rate or blood pressure.
The rebound effect is another common side effect of ADHD medication, whereby your mood shifts and energy levels drop as the medication starts to wear off.
Some non-stimulant medications cause psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression and suicidal ideation, while stimulants can be habit-forming, leading to substance use disorder (SUD) if you misuse them.
While methylphenidates have a lower potential for addiction than amphetamines, abusing drugs from both categories can make it difficult for your brain to naturally produce dopamine, driving you to use more to experience pleasure. Stimulants also have intense withdrawal symptoms, making it difficult to go without using them.
To avoid addiction when receiving treatment for ADHD, you should only take the recommended dose of ADHD medication. Don’t try to obtain a fresh prescription through unofficial channels or increase your dosage without consulting your physician. Most importantly, if you develop a dependency on the drugs, seek help from addiction specialists.
FHE Health is an accredited organization that offers effective treatment and monitoring for ADHD. Our specialists can help you find the right ADHD medication and teach you how to manage symptoms without experiencing harmful substance abuse issues. Contact FHE today to learn about our holistic approach to ADHD treatment.