
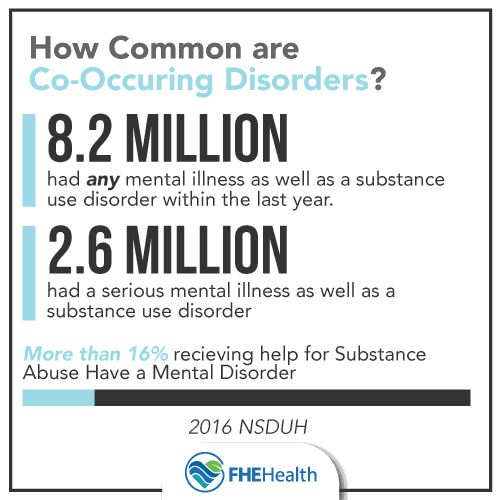
According to the 2016 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), approximately 8.2 million American adults had a mental illness as well as a substance use disorder within the past year. The same study also documented a co-occurrence of serious mental illness and the presence of substance use disorder within 2.6 million American adults.
Co-occurring disorders, also known as dual diagnosis, refer to the combination of substance abuse and the presence of a mental disorder. Over 16% of individuals receiving substance abuse treatment have also been diagnosed with a co-occurring mental disorder. More often than not, these disorders are diagnosed as two completely separate and unrelated issues. if left untreated, the symptoms of both disorders can increase in severity and be almost impossible to manage.
Here are some common co-occurring disorders that are diagnosed concurrently with substance abuse disorders:
90% of suicide victims have a mental health disorder, most commonly depression or PTSD. It is not uncommon for those who are suffering from a major depressive disorder to contemplate, attempt, or even fall victim to suicide. Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder has also been linked with suicidal ideation, as a result of exposure to severe injuries or trauma. Feelings of extreme hopelessness, agitation, fear, panic attacks, and loss can ultimately exasperate substance abuse issues may lead to further suicidal thoughts/feelings. It is vital for individuals to receive the proper diagnosis and treatment for all possible mental health disorders along with receiving treatment for his/her addiction.
Addiction, Mental Health, and Suicide
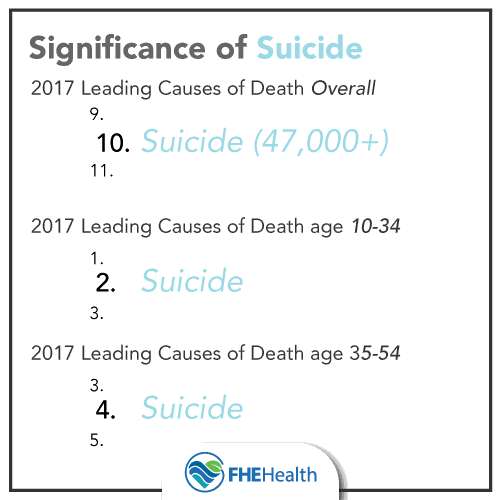 According to the 2017 reports conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), suicide was the tenth leading cause of death overall in the United States, claiming the lives of over 47,000 people. Additionally, suicide was the second leading cause of death among individuals between the ages of 10 and 34, and the fourth leading cause of death among individuals between the ages of 35 and 54.
According to the 2017 reports conducted by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), suicide was the tenth leading cause of death overall in the United States, claiming the lives of over 47,000 people. Additionally, suicide was the second leading cause of death among individuals between the ages of 10 and 34, and the fourth leading cause of death among individuals between the ages of 35 and 54.
Statistics relating to suicide aren’t intended to cause fear; they are intended to increase awareness. When substance abuse, mental health, and suicidal issues go undetected, consequences can be fatal. Awareness and information encourage positive action.
Suicide, addiction, and substance abuse have a very intertwined relationship. Just as depression and suicidal thoughts are often linked, addiction and depression often overlap. The rate of depression is commonly higher amongst addicts than the general population. The relationship between substance abuse and depression is a very complicated cause-and-effect process. Initially, determining the root of the depression can be a seemingly impossible task and isn’t necessary for the recovery process. Both issues must be treated simultaneously in order to achieve complete and maintain long-term mental, spiritual, and physical health.
Treating addiction, alone, can be a daunting task. Dealing with substance abuse disorder and mental health issues can seem impossible for the individual entering treatment. Rather than just focusing on the addiction, dual diagnosis treatment centers focus on treating the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. Here are six benefits of seeking dual diagnosis treatment.
Mental Health Priority
When entering a dual diagnosis treatment center, the first step is to address any underlying mental health disorders. Often times, addiction is propelled by an untreated mental health disorder or mental health disorders can be propelled by addiction, thus the cycle continues. A psychiatric evaluation can help the patient and the care providers create a treatment plan that is based solely on the individual needs of each patient. An individualized treatment plan may include individual psychotherapy, appropriate medication, group therapy, implementation of CBT/DBT, trauma therapy, and even educating the individual on their diagnosis while teaching him/her healthy coping skills when dealing with their mental health disorder.
Establishing Healthy Coping Skills
Another benefit of dual diagnosis treatment is educating the patient on their disorders. Once treatment has begun, specialists can teach the individual how to cope. Most patients enter treatment without a clue on how to deal with triggers, old trauma, and stressors.
(CBT) is a short-term psychotherapy that promotes problem-solving skills. Cognitive behavioral therapy primarily focuses on solutions rather than revisiting old problems. This method of therapy encourages the development of new coping strategies, changing detrimental cognitive thinking, and problem-solving skills. CBT has also been used in treating co-occurring disorders as well.
(DBT) works to address co-occurring disorders simultaneously. Enhancing behavioral skills, through mindfulness and emotional regulation, is the primary focus of DBT. This type of treatment encourages stress management, decreases impulsivity, and aims to strengthen self-esteem through discipline and structure. The goal is to replace old, self-destructive behaviors with new, healthy coping skills.
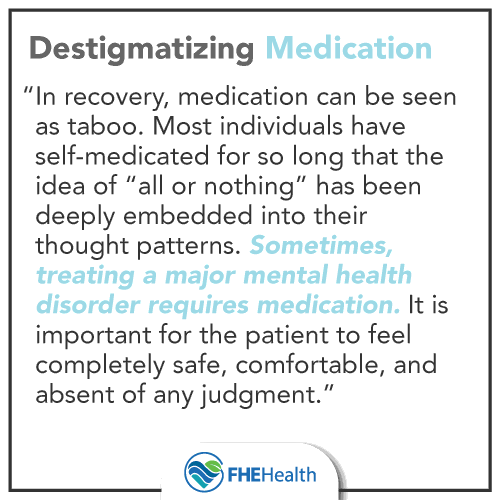
De-stigmatizing Medications for Mental Health
In recovery, medication can be seen as taboo. Most individuals have self-medicated for so long that the idea of “all or nothing” has been deeply embedded into their thought patterns. Treatment centers addressing co-occurring disorders seek to address mental health first (with medication if necessary) and then begin treatment with a clear mindset. Sometimes, treating a major mental health disorder requires medication. It is important for the patient to feel completely safe, comfortable, and absent of any judgment.
Individual and Group Therapy
One of the most important benefits of dual diagnosis recovery is therapy. While in treatment, the patient can receive individual and group therapy daily. Many different therapy options are given for each client, based on their individual needs. From intense psychotherapy, trauma therapy, EDMR, interactive group therapy, DBT, family therapy, and grief therapy are all helpful methodologies that cultivate healing for individuals suffering from co-occurring disorders.
Trauma Therapy is a vital form of therapy used for addiction treatment. Recent studies have shown that half of the adults have experienced some form of trauma in their childhood. Unresolved trauma is a leading cause of substance abuse. Addicts turn to drugs/alcohol to self- medicate the pain of PTSD. Trauma therapy requires the patient to identify the trauma by creating a safe environment for the individual to share painful experiences. Once the patient has identified trauma the therapist will incorporate tools useful in helping to process, change old belief systems, and promote healing.
Suicide Prevention
A major component of suicide prevention is safety, support, and connection. Dual diagnosis treatment centers are not limited to individuals struggling with substance abuse disorder. There are many programs in place to assist with suicide prevention. This specific method of treatment offers a number of different therapies and techniques to encourage connection, address mental health disorders, and prevent suicidal ideation. Mental health professionals can provide support and encourage an individual who may be feeling hopeless and struggling with suicidal thoughts.
Mind, Body, and Soul Healing
Most dual diagnosis treatment centers focus on all-encompassing, holistic healing: mind, body, and soul. Yoga, exercise, meditation, healthy eating, and 12-step programs can help each patient create a balance, establish spiritual growth, and produce a strong foundation for maintaining long-term sobriety.
Practicing mindfulness comes in many forms. The idea of “living in the moment” is hinged upon mindfulness. Stepping back, taking an objective view, and accepting things exactly as they are, is the best way to practice mindfulness. Mindful eating, moving meditation (yoga/tai chi), and mindful breathing are other ways to implement this practice into an individual’s daily routine. Mindfulness has been attributed to lowering feelings of anxiety/depression, controlling the body’s reaction to stressors, aiding in pain management, and identifying/processing emotions.
When embarking on the road to recovery, it is most important for the individual to find a treatment center that best suits their individual needs. Dual diagnosis treatment has proven to be effective when traditional methods of treatment have failed. Evidence has proven that recovery is a lifelong process that requires maintenance and consistent spiritual and individual growth. Therapy is an effective tool used in cultivating the foundation for long-term recovery and mitigating the symptoms of underlying mental health disorders as well as substance abuse issues.






