
In recent years, we’ve seen that violent can erupt almost anywhere—from homes and schools to churches and workplaces. Workplace mental health may be one component at play: In high-stress situations, any employee can be at risk of breaking down. On the other hand, violence affects mental health, placing an especially great burden on those who have trouble coping with the stress.
Is Workplace Violence Common?
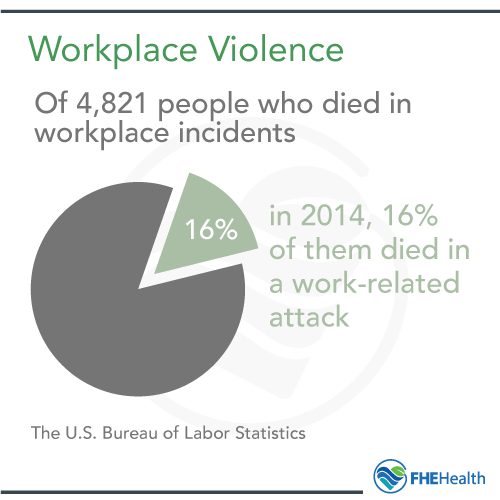
Workplace violence is more common than many realize. According to the National Safety Council, violence is the third-leading cause of death in some industries. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that about 16% of the 4,821 people who died in workplace incidents in 2014 did so because of work-related violence.
Types of Workplace Violence
 Workplace violence can include workplace trauma, in which injuries occur, and mental health abuse, such as verbal abuse. Also, experiencing a violent act in the workplace can lead to a PTSD incident years later.
Workplace violence can include workplace trauma, in which injuries occur, and mental health abuse, such as verbal abuse. Also, experiencing a violent act in the workplace can lead to a PTSD incident years later.
The deadliest events involve an active shooter in the workplace, according to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security. However, there are other causes, including coworker-related incidents and personal relationship problems. In some careers such as health care, patients are a significant cause of work-related injuries and violence.
Consider the following types of workplace violence and why they may happen.
Criminal Intent
Criminal intent violence occurs when there is no established relationship with the business, and the motive is theft. Those workers who handle cash, work alone and work late hours are at the highest risk in these situations.
Customer and Client
Customer- and client-related violence occurs when the perpetrator is a client of the employer, and the incident occurs during the worker’s normal activities on the job. Health care and social service workers face the most risks here.
Worker-to-Worker
A current or a former employee commits worker-to-worker violence. Often, the motivation comes from poor relationships with another person or a work-related conflict. Workplace trauma and losses can also trigger an event.
Domestic Violence in the Workplace
In this situation, a non-employee creates a violent situation when they attack an employee. A common situation occurs when a spouse or abuser targets an employee. Women are more likely to suffer this type of violence.
Ideological Violence
In this form, the violence is meant to target a specific organization for political, religious or ideological reasons. It can impact the property, employees or organization in whole. Extremists are the usual perpetrators.
How Violence Affects Mental Health
 Violence is a traumatic event. It doesn’t matter if it occurs just one time or happens repeatedly. Because violence can create such a jarring effect on the well-being of any individual, it can trigger mental health situations in many.
Violence is a traumatic event. It doesn’t matter if it occurs just one time or happens repeatedly. Because violence can create such a jarring effect on the well-being of any individual, it can trigger mental health situations in many.
Individuals who are predisposed to mental health conditions, such as those who have a genetic link, are at an increased risk of suffering from the negative impact of workplace violence.
When a person witnesses or is involved in a violent act, their brain chemistry changes. Without proper treatment and support, anyone who experiences this type of situation can develop mental health concerns.
Understanding how violence affects mental health is important. In the short term, violence makes it hard for a person to sleep. They may seem fine initially, but the victim of violence, especially in repeated forms, can become depressed.
They can struggle with constant stress, which can lead to health problems such as chronic pain and heart issues. Some people may develop immune system deficiencies as well.
Workplace Trauma
About half of all women who suffer from mental illness, such as anxiety, depression or post-traumatic stress disorder, have been exposed to physical or sexual abuse. Domestic abuse is commonly associated with the development of mental health concerns. Those same types of situations can play out in the workplace as well.
Consider a few examples:
- A woman suffers an injury from an angry customer. A person threatens her, pushes her and perhaps causes severe injury.
- Two coworkers get into an argument. It escalates to physical violence. One uses a knife on the other.
- An individual is repeatedly exposed to violence and verbal abuse throughout their career. Over time, this wears them down, creating mental health concerns.
- A former employee, angry about losing their job, enters the workplace and uses a gun to shoot the manager.
- A person comes into the hospital emergency room in a violent rage, lunges at and hurts a nurse.
In these situations, the individual is faced with the events of that single day as well as the long-term impact of the violence. The way a person is involved in handles and works through the exposure to violence impact their ability to protect their mental health. In most situations, violent acts like this create lasting memories that are hard to stop seeing and experiencing.
What Are the Mental Health Effects of Violence in the Workplace?
 Individuals who experience emotional, physical or sexual assault, or any violent action, are at an increased risk of developing a wide range of mental health problems. If you’ve witnessed or are a victim of workplace violence, you may be dealing with a wide range of emotions, such as:
Individuals who experience emotional, physical or sexual assault, or any violent action, are at an increased risk of developing a wide range of mental health problems. If you’ve witnessed or are a victim of workplace violence, you may be dealing with a wide range of emotions, such as:
- You feel guilt or shame over what happened.
- You’re struggling with feelings of numbness, almost as though the world feels different.
- You may be anxious about going to work.
- You may develop depression, especially if you’re predisposed to it.
No matter what happened, you may feel personally hurt by it. Abusive situations and single instances of violence make individuals see the world in a different light. Sometimes, it’s not possible to rationalize it, and in other cases, it creates changes in the way you think and experience life around you.
This leads to long-term mental health challenges. Every person’s experiences are a bit different, but the effects of violence at work may include:
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
This is perhaps the most common mental health effect from violence. Violence in the workplace has a similar impact as violence on a battlefield or in a shooting scenario. PTSD occurs when someone experiences traumatic, shocking and scary situations, often with those instances leading to harm or a person fearing for their life.
Negative thoughts develop. They replay what happened over and over again in their mind. A PTSD incident, such as an outburst, panic attack or violent reaction can also occur, worsening a person’s mental health.
Anxiety
Some individuals experience the effects of violence at work through anxiety. They struggle with the thought of going to work. Even if the threat is no longer there, they still feel anxious, worried and nervous about experiencing it.
Panic attacks occur. This often involves a sudden fear of impact from the events of the past. It may make it impossible for them to work until they receive treatment.
Depression
For those predisposed to depression, any violence in the workplace can trigger the onset or worsening of symptoms. Depression makes them feel unable to live, unable to cope and unwilling to keep going through the day.
It can be nearly impossible to stop negative thoughts. Depression is a serious health condition requiring medical help. A violent incident at work can trigger thoughts of self-harm in those with preexisting depression.
Dangerous Coping Mechanisms
Many people who struggle with mental health problems due to workplace violence look for ways to cope. They may not speak out about it and may not seek treatment. Instead, they turn to other coping mechanisms, including unhealthy ones.
The use of drugs and alcohol are widespread. Other people isolate themselves, shutting themselves away from potentially painful situations. In nearly all cases, individuals who don’t treat the mental health concerns they experience can suffer long-term damage.
It doesn’t just go away without therapy and support. If you see this happening within yourself, take action right away.
How Employers Can Prevent Workplace Violence
Workplace violence happens, but there are a variety of ways employers can work to limit it.
Minimizing Risks of Violence
According to the Alice Training Institute, which trains schools and organizations on how to remain safe, employers can do several things to reduce workplace violence. Some recommendations include:
- Have policies in place that prevent harassment in any form.
- Create a line of communication and use it to let individuals report claims and concerns safely.
- Host awareness and training sessions to teach people how to prevent violence.
- Ensure a zero-tolerance policy is in place for any instances of violence.
- Create a positive workplace culture that encourages workers to accept all others.
- Intervene sooner to prevent conflict situations from becoming violence incidents.
Providing Help After an Incident Occurs
It’s very important to understand the toll violence in the workplace takes on overall mental health. Individuals who face violence daily are at a high risk of developing mental health concerns.
After an incident occurs, many people need help managing the outcome. This may include:
- Creating immediate counseling opportunities for victims of violence
- Establishing an open environment for talking about what happened
- Setting up peer groups to help support each other after such incidents
If workplace violence occurs in your business, the way you react to it can improve the outcomes for your employees. A strong, supportive system is critical.
This is a good time to connect with our counselors at FHE Health to encourage one-on-one support and immediate assistance for potential PTSD occurrence. There’s no way to offer too much help.
Getting Workplace Mental Health Support
It’s critical for employers to monitor workplace mental health. Even in the most well-established and respected area, there’s a risk that trauma and violence can occur. When it does, it requires careful attention and treatment.
Individuals struggling with this type of scenario should seek mental health rehab. Solutions are available that can help you get back your life again.
Contact FHE Health for Immediate Help
To learn more about mental health rehab, speak to our team at FHE Health. No matter what you have been through, we offer treatment options to improve your wellbeing. Call to speak to one of our counselors now at (833) 596-3502.






