Alcohol is a chemical that can change the physical makeup of the body. People often say that alcohol makes your body older. How can drinking a few glasses of alcohol a week prematurely age you? It may be a bit more complex than you realize. And, while you may believe that alcohol is safe to consume, it’s also important to recognize the value of setting limits.
Is Alcohol Bad for You?
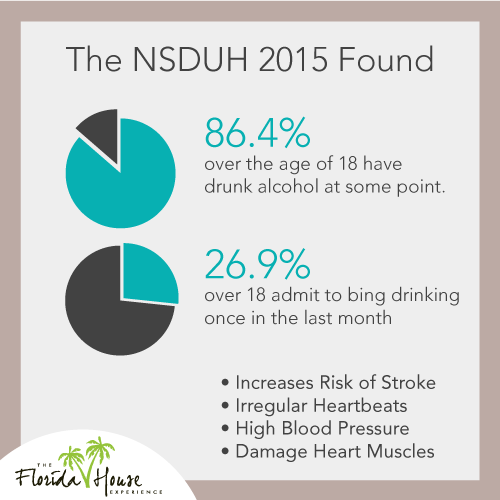 It is, of course, perfectly legal and quite common for people to consume alcohol. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health from 2015 found that 86.4 percent of people over the age of 18 have drunk alcohol at some point. It also found, however, that 26.9 percent of people over the age of 18 admitted to binge drinking at least one time in the previous month. It’s this heavy usage is likely to cause rapid aging of the body.
It is, of course, perfectly legal and quite common for people to consume alcohol. The National Survey on Drug Use and Health from 2015 found that 86.4 percent of people over the age of 18 have drunk alcohol at some point. It also found, however, that 26.9 percent of people over the age of 18 admitted to binge drinking at least one time in the previous month. It’s this heavy usage is likely to cause rapid aging of the body.
Alcohol consumption, especially if drinking too much, impacts various systems of the body. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism states the following changes occur in the body when alcoholism is present:
- Long-term drinking can damage the heart muscle, causing cardiomyopathy, which limits the muscle’s ability to function.
- It increases the risk of strokes.
- It causes high blood pressure in many patients.
- It can lead to irregular heartbeats.
In the liver, it also can cause a number of health issues including steatosis or fatty liver, cirrhosis, fibrosis and alcoholic hepatitis. It can cause the pancreas to produce toxic substances, leading to inflammation and swelling of the blood vessels, limiting good digestion.
How Alcohol Makes You Age
The impact on your health is one thing, but for many people, the implications on the way you feel and how young you look is very different. Take into consideration a few of the most common implications to aging.
Muscles Become Fattier
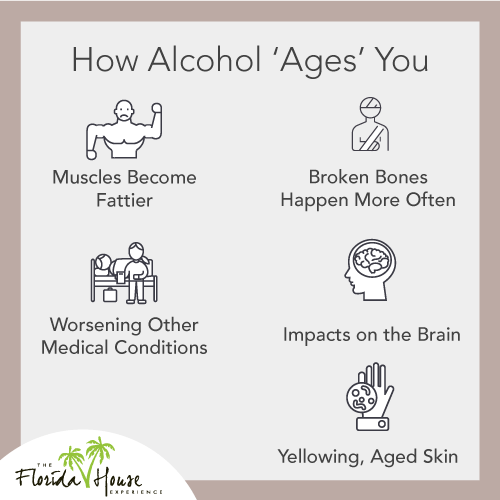 Alcohol causes hormone changes in the body. Some of those changes cause the amount of fat in your body to grow while the amount of muscle tissue decreases. Even if you don’t lose or gain any weight, you may notice your body is less tense and toned and fattier. This change has long-term implications. For example, it can:
Alcohol causes hormone changes in the body. Some of those changes cause the amount of fat in your body to grow while the amount of muscle tissue decreases. Even if you don’t lose or gain any weight, you may notice your body is less tense and toned and fattier. This change has long-term implications. For example, it can:
- Increase your blood pressure
- Reduce your ability to react as fast as you used to
- Slow your ability to move quickly
All of these are common in older people. For those who drink excessively, they can occur sooner.
Broken Bones Happen More Often
Alcohol inhibits the brain’s ability to keep the body in balance. This causes a significant number of accidents each year when people fall or lose their balance. This also directly increases the risk of being involved in a car accident.
Individuals who fall are more likely to have hip fractures or suffer from broken bones. And, as in older people, the immune system is somewhat limited. This can slow the healing process as well. And since you may have a lack of coordination and slower reaction time, this, too, increases the risk of accidents leading to broken bones.
Yellowing, Aged Skin
The skin is one of the most common aspects of defining a person’s age. As a person gets older, the skin ages by losing some of its collagen. In individuals who are heavy drinkers, this process speeds up. In many cases, those who drink even on a routine basis may experience changes to the way their skin looks. You may have a yellowing of the eyes and skin, too — an indication of alcoholic liver disease.
For others, heavy drinking causes:
- The development of wrinkles on the skin
- Dry and cracked-looking skin
- Puffiness in some areas
- Red Cheeks
- Purple lines or spots on the skin due to burst capillaries
You may notice your skin feels thinner and there are more pronounced wrinkles around your eyes.
Worsening Other Medical Conditions
Another way that alcohol ages your body are by speeding up the effects and symptoms of other medical conditions you may have. For example, if you suffer from diabetes, you may see alcohol cause a significant drop in blood sugar levels. This can create a life-threatening scenario called hypoglycemia, which can last as long as 24 hours after drinking alcohol.
In other people, such as those who have a heart condition, it can worsen symptoms of high blood pressure. If you suffer from ulcers, alcohol can worsen those symptoms as well, limiting the ulcer’s ability to heal and creating searing pain in the area.
Impacts on the Brain
Another important way alcohol ages the body is by impacting the health of the brain. Heavy drinking long-term can cause shrinkage in the brain volume. This occurs simply because of the impact of the chemical on brain tissue. When the brain’s volume decreases, it causes a wide range of symptoms including, according to Scientific American:
- Limited cognitive function
- A decrease in memory quality
- Dementia-like symptoms such as mental confusion
- Lack of muscle coordination
- Agitation
These are common symptoms that occur in people as they get older. For those who drink heavily, though, they can occur much sooner.
Can This Be Reversed?
Is it possible to reverse this type of damage? That depends. For example, damage to the skin and tissues may improve when a person stops using drugs and alcohol. The liver can heal itself in a matter of years if the proper steps are taken. The immune system, which tends to have limited functionality when a person is drinking heavily, can get back to work once the toxins are out of your body. These are all very good things. Many people feel and look healthier once they’ve stopped using alcohol for a month or more.
Yet the damage alcohol does to your heart, brain, and other organs is hard to repair. In some cases, long-term alcohol use makes it impossible for an individual to see improvement, especially in areas such as heart function, diabetes control, and overall brain well-being.
Getting Help for Alcoholism Is the First Step
While alcohol damage has a wide range of implications, many of which can be life-changing, you can significantly improve many of these factors by working through detox and eliminating alcohol consumption. With the help of our team at FHE Health, it may be possible to achieve this goal more easily than you think. Contact us to learn more about the treatment options available to you.






