
Imagine a healthy young athlete in the prime of his life. He’s a football star, well known in the community for his enthusiasm and ability to dominate on the field. He’s had a concussion before, but what football player hasn’t? In the weeks after the season wraps up, family and friends note he’s a bit depressed and seems sad quite often. They believe it’s the result of the season ending, but it could be something much more. Suddenly, the news breaks of his death. A young star is gone, and they believe it was suicide. How can this happen?
There’s growing evidence that links mental health and concussions. Changes in mental health after concussion injuries may include depression, thoughts of suicide and anxiety.
Mental Health After Concussion: What Is the Link?
Studies indicate that individuals who suffer a mild head injury are at high risk for adverse mental health symptoms. Concussions are a form of mild head injury, often occurring as a result of traumatic force against the skull that causes the brain to move and violently hit the skull wall. The damage from a concussion ranges from minimal, creating no outward signs of damage, to the loss of consciousness and, in some cases, sudden death.
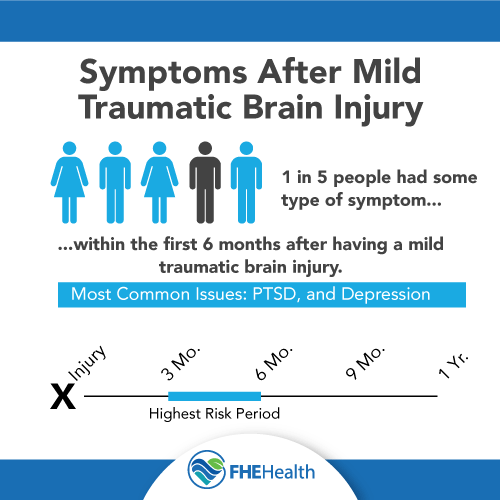
Specifically, a study conducted by the National Institutes of Health found that 1 in 5 people had some type of symptom within the first six months after having a mild traumatic brain injury, including post-traumatic stress disorder and major depressive disorder. The highest risks came between three and six months after the injury, making it hard to correlate the two.
What Are the Known and Suspected Effects of Concussions?
Concussions seem like a simple injury to tissue, much like a sprain or damage to a muscle ligament. Yet they are much more. Concussions can impact the brain’s complex connectivity and various components for not just a short amount of time, but for decades.
In the short term, concussions create numerous effects, such as:
- Headaches
- Vision changes
- Fatigue
- Feelings of brain fog
- Ringing in the ears
- Sensitivity to light and sound
Over time, longer-term effects can occur, often creating lasting changes in the physical structure of the brain. Some of these concussion effects include:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Problems with memory
- Sensitivity to light and sound
- Irritability and personality changes
- Disorders or changes to smell and taste
- Depression and mental health disorders
Understanding the Impact of Concussions and Mental Health
Researchers continue to look for this link, aiming to understand the underlying cause and treatment options.
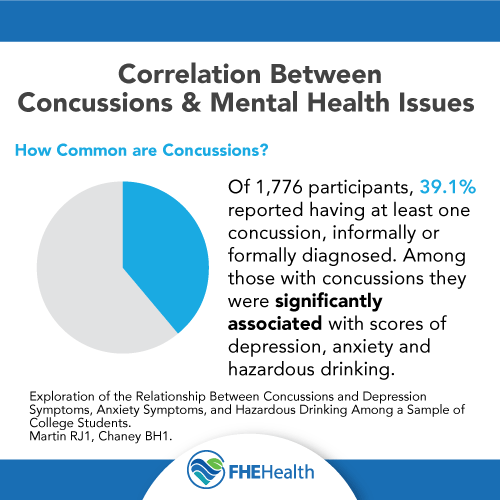
One study published in the U.S. National Library of Medicine found a correlation between athletes with concussions and depression risks. It found 39 percent of those athletes who reported having at least one concussion had some type of anxiety, depression or other mental health disorder. It also found that only hazardous drinking of alcohol was a more common factor in the development of depressive symptoms.
Another study also published in the U.S. National Library of Medicine showed that multiple concussions could contribute to late-onset major depression disorders. However, it found that playing sports can actually help combat depressive symptoms in those predisposed to the condition. This can make it hard to pinpoint the underlying cause.
There is an increasing number of reports of the impact of concussions. Recently, Olympic cyclist Kelly Catlin, who was just 23 years old and recently graduated from Stanford University, committed suicide. Her family believes concussions months prior to the incident contributed to her depression.
The National Football League has conducted its own research on the impact of concussion on football players. It’s implemented increasing amounts of protection for players to manage symptoms as quickly as possible.
What Can Be Done About Concussion?
The first and most important step is to acknowledge something isn’t right. Then, seek treatment. The brain is a constantly changing, incredible machine. Even if your brain is damaged by a concussion, you don’t have to live with depression. Treatment can help to improve your quality of life and alleviate much of the stress you feel.
Can NeuroRehab Help?
NeuroRehab may offer helpful treatment for those facing depression and anxiety following a mild traumatic brain injury. Using NeuroFeedback training, EEG brain mapping, brain stimulation therapy and other rehabilitative services, corrections to the changes in the brain caused by this type of injury may be possible. Patients receive a customized treatment plan that pinpoints areas of change. A personalized treatment plan allows for the very best level of treatment possible.
Traditional Depression Therapy
While these innovative types of treatment are beneficial and perhaps most impactful for many patients who are battling depression, there is still an important role for traditional depression therapy. It can improve the overall quality of life while also reducing the risk of major depressive orders.
Traditional depression therapy may include cognitive therapy treatment, which pinpoints specific negative thought patterns and helps an individual to overcome them by making different choices. It may include the use of medications. Some patients also benefit from treatment through counseling sessions and individual and group therapy.
When Should You Seek Help for Concussions and Mental Health Disorders?
 Not every person who experiences a concussion develops depression. More so, many people who do become depressed may struggle to make the link between the two conditions. There are some key signs to look for that can indicate a person needs additional treatment and a formal diagnosis. If you or your loved one has suffered a concussion, look for signs that could indicate mental health disorders:
Not every person who experiences a concussion develops depression. More so, many people who do become depressed may struggle to make the link between the two conditions. There are some key signs to look for that can indicate a person needs additional treatment and a formal diagnosis. If you or your loved one has suffered a concussion, look for signs that could indicate mental health disorders:
- Significant changes in personality; don’t overlook this in teens, especially those who may be moody
- Trouble with grades in school; at work, changes in work focus and ability to concentrate
- Changes in memory habits such as forgetting appointments or forgetting important information
- Vision changes, especially blurred vision that seems to come and go without warning
- Depression-like feelings such as worthlessness and sadness that don’t improve with activities you once enjoyed
If you experience these types of changes, do not hesitate to reach out for help. Turn to a specialist that offers NeuroFeedback Training as well as other forms or NeuroRehab, which can provide better diagnostics than traditional forms.
What Can You Do About Concussion and Depression?
Anyone who exhibits any type of depression-like symptom needs to seek treatment. Feeling sad for a short period of time may seem normal. Yet, when it impacts the quality of life or lasts a long time, it can be life-threatening. If you have had a concussion and suicidal thoughts, please seek immediate medical help.






