Find out some of the many personal factors that contribute to substance abuse and how you can seek help to reduce your risk of addiction.
Understanding the personal factors that contribute to substance abuse can help individuals avoid risky behaviors when predisposed to addiction. These five risk factors that lead to substance abuse often result from the environment and circumstances in which a person grows up. As such, many risk factors may be beyond their control at a young age. However, knowing that you are at a greater risk of developing a drug addiction due to your circumstances can let you make the right choices for your long-term health and well-being.
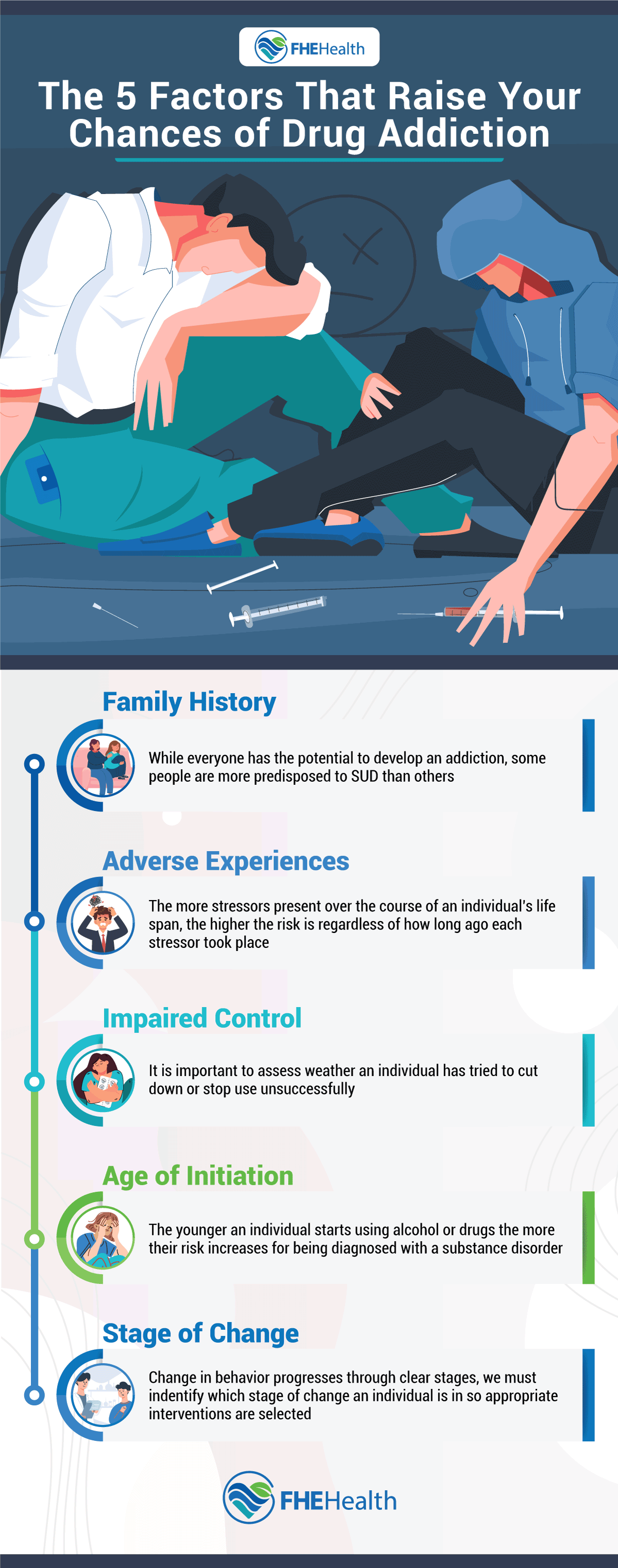
Personal Factors That Contribute to Substance Abuse
According to the National Institutes of Health, 10% of American adults experience a substance abuse disorder at some point in their lives. No definitive five factors guarantee you’re at an increased risk of addiction. However, many factors have proven to heighten the chance of substance abuse.
1. Community Poverty
The conditions in which a person grows up and their economic status are risk factors for substance abuse. A 2021 Swedish study concluded that exposure to living in poverty in early life is a risk factor for developing drug addiction in adulthood. In particular, the study found that males and females who moved into poverty during adolescence were at the highest risk of substance abuse.
2. Availability of Drugs at School
Peers and school significantly impact an individual’s risk of developing drug addiction later in life. A student’s friends and peers have a major influence on them during their teenage years, especially people who have low self-esteem or are socially insecure. Their peers may pressure them to try drugs at a young age. When these substances are widely available in a school environment, students at this vulnerable age are more likely to try them and develop an addiction. A 2021 study identified high school as a critical risk period for drug addiction and substance abuse.
3. Lack of Parental Supervision
A teenager’s relationship with their parents and a household’s level of parental monitoring are also risk factors for drug addiction. Teenagers who don’t have close relationships with their parents may live in a household with familial conflict, where their parents place unrealistic expectations or pressure on them, or they may even face physical, emotional or sexually abusive relationships with their parents. A 2016 study indicates that people who experienced childhood trauma or abuse are 1.5 times more likely to have abused illicit drugs in the past 12 months than those who did not.
Even in households where parents and their children have healthy relationships, if there is a lack of parental supervision, children have a higher chance of drug addiction. Studies suggest that adolescents with inadequate parental supervision are more likely to engage in drug abuse and alcohol use. A 2005 study found that in adolescents undergoing treatment for alcohol use disorders, individuals with parental neglect were less likely to be free of these symptoms within a 12-month period than those who had parental involvement.
4. Aggressive Behavior During Childhood
Aggression from a young age is widely accepted as a risk factor for substance abuse later in life, based on several studies. One 2016 PubMed study found that instances of early childhood aggression were directly related to the age when an individual began abusing drugs. For example, substance abuse by age 14 was found to correlate with children’s personalities during their preschool years.
5. Drug Experimentation
While some teenagers and young adults may believe that experimentation with drugs is harmless and part of growing up, the reality is that early drug experimentation increases the chances of developing an addiction. Experimenting with drugs doesn’t automatically result in lifelong addiction but can increase the number of risk factors a person has that make them more vulnerable to addiction. Avoiding substance use and experimentation altogether is the safest way to reduce the risk of developing a drug addiction. This is especially vital if you’re aware of a genetic predisposition to addiction.
Biological vs. Environmental Risk Factors
Many factors that increase a person’s risk of addiction are environmental. When combined, these external life factors create a situation where someone is more likely to engage with and become dependent on a substance. However, biological predisposition to addiction is another significant risk factor to be aware of. If you’re genetically at risk of alcohol or drug addiction, knowing this from a young age can help you make smart choices that keep you on a path of avoiding substance use.
According to the National Institutes On Drug Abuse, gene expression (epigenetics) accounts for 40–60% of an individual’s risk of developing addiction or substance use disorders. Other biological factors beyond their genes include a person’s gender and mental health disorders. Having a mental health condition increases the risk of substance use disorders. One research report suggests that while men are more likely to develop a dependence on drugs, women are more susceptible to experiencing cravings, which can perpetuate the cycle of addiction.
The combination of biological and environmental risk factors a person possesses or is exposed to during their early childhood and teenage years impacts their chance of engaging in substance abuse and developing addiction in adulthood. If you’re dealing with addiction, it’s critical to seek professional help from an accredited facility like FHE Health in southern Florida.
You Can Make a Change Today
Even individuals who possess three or four factors that contribute to substance abuse have the power to make choices that better their long-term health. Regardless of your circumstances, it’s never too late to seek help to overcome addiction.
At FHE Health, our dedicated team of counselors can help you initiate your journey to recovery. We offer inpatient addiction programs to support you through the detox process and a variety of therapy and neurorehabilitation services to meet your needs. Call FHE Health today at (844) 299-0618 to speak to a professional about your options for addiction treatment.