
“Cannabidiol” (CBD), or “hemp oil” may seem like a new discovery, but it has actually been cultivated for thousands of years. Many cultures, including the ancient Egyptians, used the cannabis plant and its derivatives for healing, and cannabis was most likely one of the first plants cultivated for the purpose of making cloth.
Often there is confusion about CBD and whether it is marijuana or if it has “tetrahydrocannabinol” (THC), the psychoactive component that creates a “high.” The easiest way to understand the difference is to think of cannabis sativa as the “mother” plant, and then hemp and marijuana as her two different children. Basically, CBD products are extracted from either hemp plants that contain hardly any THC, or from marijuana plants that are high in THC.
What Is CBD?
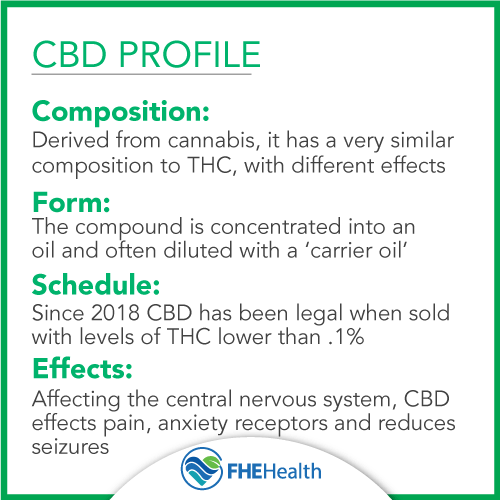 CBD is a “phytocannabinoid” found naturally in cannabis plants (again, both hemp and marijuana). When cannabinoids are consumed, they interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a range of effects. Endocannabinoid receptors occur naturally throughout the entire body, and help to control pain, inflammation, mood, memory, and more. At room temperature, cannabidiol is a colorless crystalline solid.
CBD is a “phytocannabinoid” found naturally in cannabis plants (again, both hemp and marijuana). When cannabinoids are consumed, they interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a range of effects. Endocannabinoid receptors occur naturally throughout the entire body, and help to control pain, inflammation, mood, memory, and more. At room temperature, cannabidiol is a colorless crystalline solid.
CBD can be found in almost every type of cannabis plant, but below are the three major categories:
- Marijuana plants typically high in THC and low in CBD
- Industrial hemp plants high in CBD, containing no THC with no psychoactive effects
- Varieties of cannabis plants specifically bred to contain high-CBD/low-THC components
CBD has the same chemical formula as THC: 30 hydrogen atoms, 21 carbon atoms, and two oxygen atoms; but the atoms are in a different arrangement. THC has the psychoactive component that creates a high or euphoria, while CBD does not have this active ingredient. CBD can in fact interfere with THC and dampen the psychoactive effect.
 Cannibinoids work in the body by binding to certain receptors, either CB1 or CB2. CBD is thought to bind to CB2 receptors, which are more common throughout the immune system than CB1 receptors, which are more specific to the central and peripheral nervous system. THC activates the CB1 receptors.
Cannibinoids work in the body by binding to certain receptors, either CB1 or CB2. CBD is thought to bind to CB2 receptors, which are more common throughout the immune system than CB1 receptors, which are more specific to the central and peripheral nervous system. THC activates the CB1 receptors. There are many CBD products on the market and thus a variety of ways in which CBD is taken:
There are many CBD products on the market and thus a variety of ways in which CBD is taken:







