
|
|
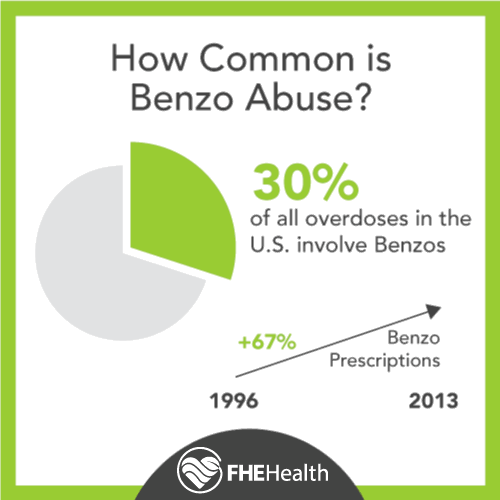
Benzodiazepines, often called benzos, are a type of highly addictive drug. Doctors prescribe them for the treatment of insomnia because they work to calm a person. They can also have a sedative effect, making them ideal for a person seeking to treat anxiety or high stress levels.
Many people try to stop using benzos on their own. This may prove very difficult due to the intense benzo withdrawal symptoms.
What Happens During Benzo Withdrawal?
 Trying to benzo detox at home is not only likely to fail but also highly risky. Benzos interact with the central nervous system, depressing it to control seizures, anxiety and insomnia. When you try to remove this type of drug quickly or without medical supervision, the body can enter a state of shock. In some cases, this can create life-threatening symptoms such as seizures, suicidal thoughts, depressed respiration and sudden cardiac death.
Trying to benzo detox at home is not only likely to fail but also highly risky. Benzos interact with the central nervous system, depressing it to control seizures, anxiety and insomnia. When you try to remove this type of drug quickly or without medical supervision, the body can enter a state of shock. In some cases, this can create life-threatening symptoms such as seizures, suicidal thoughts, depressed respiration and sudden cardiac death.
A person who can’t stop using these drugs without feeling withdrawal symptoms has a chemical dependency. This indicates the body has become dependent on the drug in some form. If the amount of benzo is decreased or not available, the body exhibits numerous symptoms. Over time, the body must readjust to the lack of the drug.
What Are Common Signs of Benzo Withdrawal?
Trying to determine when benzo withdrawal starts is difficult, as the timeline varies for each person. Some people begin to see withdrawal symptoms develop within a few hours of not taking the drug. Some may also see withdrawal symptoms last for days or weeks. The severity of the symptoms depends on how much of the drug an individual is using, as well as how long the dependency has been present.
Common symptoms of benzo withdrawal include:
- Anxiety and panic attacks
- Muscle pain and difficulty moving
- Insomnia
- Irritability and mood swings
- Poor concentration
- Distortion of reality
- Nausea
- Heart palpitations
- Agitation
- Tremors
Most people will experience some of these symptoms immediately after stopping the drug.
What Are Severe Benzo Withdrawal Symptoms?
Some people may experience severe symptoms of withdrawal within just a few hours of discontinuing the drug. These include:
- Seizures
- Delirium
- Periods of psychosis
- Suicide threats
- Intense sweating
- Inability to control movements
- Very fast heart rate, which can trigger sudden death
In a controlled environment, your doctor is able to minimize risks to you should severe complications occur. Keep in mind that even your doctors don’t know if you’ll experience severe symptoms. Some people who take even small amounts of benzos can experience complications within a short time.
What Will You Feel During Benzo Withdrawal?
 Aside from these physical symptoms, withdrawal can also produce an emotional impact. The pain, for example, can create mental anguish and difficulty concentrating.
Aside from these physical symptoms, withdrawal can also produce an emotional impact. The pain, for example, can create mental anguish and difficulty concentrating.
Many people are afraid, exhausted and overwhelmed. Some become unable to sleep for days; others experience depression and anxiety. It’s possible to develop chronic depression and anxiety during the withdrawal process. Without treatment, these signs of withdrawal may not go away for some time.
Why Do Benzo Withdrawal Symptoms Make Detox Failure Common?
The intensity of the symptoms you feel, coupled with the intense emotional trauma the process can create, often leads to detox failure when attempted outside a clinical setting. Without benzo withdrawal help, most people fail the process and turn back to the drug to soothe their symptoms.
What Is the Benzo Withdrawal Timeline?
 Every patient is different. Benzo withdrawal duration depends on the type of drug used, the amount consumed and the length of the dependency. Commonly, the following can occur:
Every patient is different. Benzo withdrawal duration depends on the type of drug used, the amount consumed and the length of the dependency. Commonly, the following can occur:
- Withdrawal symptoms typically begin within 24 hours of the last use of the drug.
- They can continue from the most intense symptoms to the least intense over several months.
- The highest risk for severe reactions during withdrawal is from 24 hours after through the first week of stopping the drug.
Drugs with a shorter life cycle in the body, such as Xanax, may create withdrawal symptoms within 10 to 12 hours. Other drugs, such as Valium, remain in the body in smaller amounts for longer periods. Here, you may not notice symptoms for 2 days or more.
The method of using the drug can also play a role. People used to ingesting pills may experience a delay in symptoms. Those who snort or inject the drug, which sends it directly into the bloodstream, may see withdrawal symptoms very quickly.
Typical phases of withdrawal from benzos may include the following.
Early Withdrawal
Early withdrawal may happen within a few hours of not taking the drug. A sense of anxiety may develop early on, and fear of what’s to come is common. Feelings come back.
Acute Withdrawal
A few days later, people may begin to feel more intense physical symptoms of withdrawal. These include tension, nausea and blurred vision. This is also when seizures can occur. Some people experience hallucinations; others struggle with a lack of concentration. Cravings are strong in this phase.
Protracted Withdrawal
Many people will get through the acute withdrawal stage within 2 weeks, but it can take several months. Beyond this timeframe, though, a protracted withdrawal can occur, causing a person to never truly feel “normal” again due to the lasting impact of the drug. A person may suffer chronic depression or anxiety, have some concentration or memory issues and experience muscle pain for years after they’ve stopped taking the drug.
Getting Benzo Withdrawal Help Can Improve Outcomes
Seeking benzo rehab in Florida could be the best decision for you for several reasons. First, you’ll be in a safe setting where doctors can monitor your health. They can also provide you with medications to relieve some of your symptoms. If withdrawal is easier for you, you’re more likely to succeed in the process.
At home, benzo detox is possible only in a limited way. You may be able to see some results by meditating or taking over-the-counter pain medications. However, this rarely offers much improvement. Instead, it’s best to work with a doctor who can provide long-lasting improvement.
FHE Is Here to Help You
A full detox facility that provides medical treatment for physical symptoms can help you overcome the pain and emotional trauma caused by benzo withdrawal. Contact FHE to get started on the path to recovery today.






