
- Have you or someone you know tried to stop drinking or attempted to cut down on drinking alcohol but failed to do so?
- Do you look forward to your next drink?
- Has drinking ever interfered with your job, school or family responsibilities?
- If you abstain from drinking for more than 48 hours, do you start experiencing unpleasant physical and emotional symptoms that can be relieved only by drinking?
- Does it anger you when family or friends suggest you need to stop drinking so much?
If you answered “yes” to any one of these questions, you could be an alcoholic.
The Difference Between a Heavy Alcohol User and an Alcoholic
 The American Society of Addiction Medicine defines an addiction to drugs or alcohol as:
The American Society of Addiction Medicine defines an addiction to drugs or alcohol as:
- An inability to abstain from use
- Impaired behavioral control over using addictive substances
- Overwhelming cravings for alcohol/drugs due to suffering increased tolerance and withdrawal symptoms
- Reluctance or inability to recognize they have an addiction
- Dysfunctional emotional responses to their alcoholism or drug addiction
Alternately, a heavy alcohol user is someone who binge drinks on at least five days per month but does not drink every day or even every other day. For complex reasons involving genetics and psychosocial factors, heavy alcohol users may never evolve into full-fledged alcoholics.
Although no formal Alcoholics Anonymous definition of what constitutes alcoholism exists, AA characterizes alcoholism as a chronic disease demanding lifelong treatment and a commitment by members to abstain from alcohol completely.
What Is a High-Functioning Alcoholic?
High-functioning alcoholics are experts at leading a double life. They work hard to ensure they appear normal and successful to their family, friends and coworkers.
They dress well, seem healthy and have college degrees. In fact, you may never see a so-called high-functioning alcoholic drink excessively in public or drink in public at all.
Many high-functioning alcoholics do not experience physical withdrawal symptoms when they abstain. Instead, they suffer psychologically without alcohol to numb powerful feelings of anxiety, depression and low self-esteem. High-functioning alcoholics often need intensive psychological counseling but refuse to seek help because they don’t believe they have a mental health problem or think they will be stigmatized by going to a psychologist.
Can an Alcoholic Be a Social Drinker?
 If you deliberately limit yourself to one or two alcoholic beverages at an occasional social gathering, never allow yourself to become inebriated and do not spend hours during the day thinking about alcohol, then you are considered a social drinker.
If you deliberately limit yourself to one or two alcoholic beverages at an occasional social gathering, never allow yourself to become inebriated and do not spend hours during the day thinking about alcohol, then you are considered a social drinker.
Social drinkers are not alcoholics or high-functioning alcoholics. They do not experience adverse physical, psychological or emotional symptoms when they do not drink.
Social drinkers can have a glass of wine or a beer at the end of the day and not want another drink for days or weeks. They drink responsibility and, in most cases, do not become an alcoholic.
Alcoholics cannot be just social drinkers. Alcoholism is a medical disease that permanently changes the way the brain responds to addictive substances.
Alcoholics Cannot Control Their Drinking
If someone you know has completed an alcohol treatment program, abstained from alcohol for a period of time and thinks they can have a glass of wine or a beer without relapsing, tell them immediately they should reconsider that assumption.
Why can’t alcoholics stop drinking? Why can’t they just drink moderately? In the same way drug addicts can’t snort cocaine or inject heroin once every few weeks, recovering alcoholics cannot drink without risking relapse. Even after 10 years of sobriety, a recovering alcoholic who decides it’s safe to have”just one” drink may find themselves spiraling toward the same rock bottom they hit before entering rehab.
Alcoholism and Brain Damage
One of the main reasons why sober alcoholics should never take another drink has to do with the brain’s white matter.
White matter composes much of the brain’s deep subcortical areas. Containing axons (nerve fibers) connected to nerve cells, white matter facilitates the transmission of messages throughout the central nervous system. Axons are covered in a white, fatty substance called myelin, which gives white matter its characteristic color.
Research indicates that alcoholics have reduced areas of white matter compared to non-alcoholics. More specifically, it is damage to oligodendrocytes (cells needed to produce myelin) that causes loss of white matter and permanent disruption of communication pathways in the brain.
The more an alcoholic drinks (before and after recovery), the more damage occurs to white matter and other important brain structures, like the inferior frontal gyrus. This area regulates decision-making and impulse control, two things that are absolutely essential for eliminating the risk of becoming re-addicted to alcohol.
Repeated Alcohol Detox and Kindling
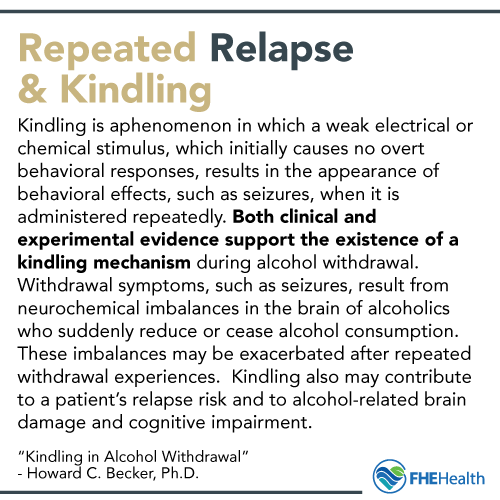 When someone undergoes multiple alcohol detox programs because they keep relapsing, there’s a possibility of increasing severity of withdrawal symptoms, a phenomenon called kindling. Alcoholics who have seizures or delirium tremens during detox are also more likely to be repeat detoxifiers. Kindling increases the risk of relapse, further permanent brain damage and cognitive issues associated with memory, focus and comprehension.
When someone undergoes multiple alcohol detox programs because they keep relapsing, there’s a possibility of increasing severity of withdrawal symptoms, a phenomenon called kindling. Alcoholics who have seizures or delirium tremens during detox are also more likely to be repeat detoxifiers. Kindling increases the risk of relapse, further permanent brain damage and cognitive issues associated with memory, focus and comprehension.
The mechanism causing kindling is the same as that behind why recovering alcoholics cannot control their drinking. Hypersensitization and desensitization of certain neuronal systems produce significant brain chemical imbalances that lead to more intense withdrawal symptoms as well as the inability of the brain to protect itself from spontaneous addiction.
High-functioning alcoholics and heavy binge drinkers also suffer deficits in self-control, emotional learning and working memory. Research shows that the toxic effects of repeatedly “withdrawing” from alcohol (abstaining from alcohol for several days before drinking to the point of passing out, as many binge drinkers and HFAs do) causes subcortical (white matter) damage. In addition, repeatedly engaging in periods of acute intoxication/acute detoxification increases the risk of severe muscle tremors and seizures.
Alcoholism Is a Chronic Medical Disease
Diabetics who eat foods containing refined flour or table sugar risk suffering complications of their disease that could require emergency medical treatment. People with high cholesterol must avoid fried, fatty foods to reduce their risk of heart attack.
Likewise, recovering alcoholics should never think they can safely drink after a successful few months or years of abstaining from alcohol. Anyone dealing with a chronic disease like diabetes, high cholesterol, high blood pressure or alcoholism needs to make consequential, minute-by-minute decisions that directly support prevention of the disease from harming their life and the lives of those they love.
Contact FHE Health today if you or someone you know needs professional, caring help for an alcohol or drug addiction.






